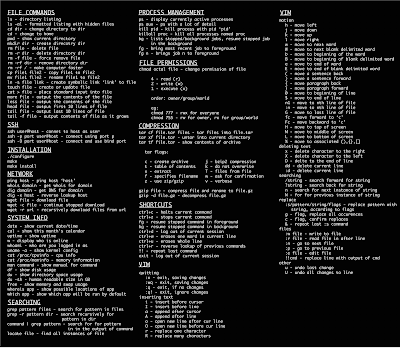
System Info
date – Show the current date and time
cal – Show this month's calendar
uptime – Show current uptime
w – Display who is online
whoami – Who you are logged in as
finger user – Display information about user
uname -a – Show kernel information
cat /proc/cpuinfo – CPU information
cat /proc/meminfo – Memory information
df – Show disk usage
du – Show directory space usage
free – Show memory and swap usage
Keyboard Shortcuts
Enter – Run the command
Up Arrow – Show the previous command
Ctrl + R – Allows you to type a part of the command you're looking for and finds it
Ctrl + Z – Stops the current command, resume with fg in the foreground or bg in the background
Ctrl + C – Halts the current command, cancel the current operation and/or start with a fresh new line
Ctrl + L – Clear the screen
command | less – Allows the scrolling of the bash command window using Shift + Up Arrow and Shift + Down Arrow
!! – Repeats the last command
command !$ – Repeats the last argument of the previous command
Esc + . (a period) – Insert the last argument of the previous command on the fly, which enables you to edit it before executing the command
Ctrl + A – Return to the start of the command you're typing
Ctrl + E – Go to the end of the command you're typing
Ctrl + U – Cut everything before the cursor to a special clipboard, erases the whole line
Ctrl + K – Cut everything after the cursor to a special clipboard
Ctrl + Y – Paste from the special clipboard that Ctrl + U and Ctrl + K save their data to
Ctrl + T – Swap the two characters before the cursor (you can actually use this to transport a character from the left to the right, try it!)
Ctrl + W – Delete the word / argument left of the cursor in the current line
Ctrl + D – Log out of current session, similar to exit
Learn the Commands
apropos subject – List manual pages for subject
man -k keyword – Display man pages containing keyword
man command – Show the manual for command
man -t man | ps2pdf - > man.pdf – Make a pdf of a manual page
which command – Show full path name of command
time command – See how long a command takes
whereis app – Show possible locations of app
which app – Show which app will be run by default; it shows the full path
Searching
grep pattern files – Search for pattern in files
grep -r pattern dir – Search recursively for pattern in dir
command | grep pattern – Search for pattern in the output of command
locate file – Find all instances of file
find / -name filename – Starting with the root directory, look for the file called filename
find / -name ”*filename*” – Starting with the root directory, look for the file containing the string
filename
locate filename – Find a file called filename using the locate command; this assumes you have already used the command updatedb (see next)
updatedb – Create or update the database of files on all file systems attached to the Linux root directory
which filename – Show the subdirectory containing the executable file called filename
grep TextStringToFind /dir – Starting with the directory called dir, look for and list all files containing TextStringToFind
File Permissions
chmod octal file – Change the permissions of file to octal, which can be found separately for user, group, and world by adding: 4 – read (r), 2 – write (w), 1 – execute (x)
Examples:
chmod 777 – read, write, execute for all
chmod 755 – rwx for owner, rx for group and world
For more options, see man chmod.
File Commands
ls – Directory listing
ls -l – List files in current directory using long format
ls -laC – List all files in current directory in long format and display in columns
ls -F – List files in current directory and indicate the file type
ls -al – Formatted listing with hidden files
cd dir – Change directory to dir
cd – Change to home
mkdir dir – Create a directory dir
pwd – Show current directory
rm name – Remove a file or directory called name
rm -r dir – Delete directory dir
rm -f file – Force remove file
rm -rf dir – Force remove an entire directory dir and all it’s included files and subdirectories (use with extreme caution)
cp file1 file2 – Copy file1 to file2
cp -r dir1 dir2 – Copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if it doesn't exist
cp file /home/dirname – Copy the file called filename to the /home/dirname directory
mv file /home/dirname – Move the file called filename to the /home/dirname directory
mv file1 file2 – Rename or move file1 to file2; if file2 is an existing directory, moves file1 into directory file2
ln -s file link – Create symbolic link link to file
touch file – Create or update file
cat > file – Places standard input into file
cat file – Display the file called file
more file – Display the file called file one page at a time, proceed to next page using the spacebar
head file – Output the first 10 lines of file
head -20 file – Display the first 20 lines of the file called file
tail file – Output the last 10 lines of file
tail -20 file – Display the last 20 lines of the file called file
tail -f file – Output the contents of file as it grows, starting with the last 10 lines
Compression
tar cf file.tar files – Create a tar named file.tar containing files
tar xf file.tar – Extract the files from file.tar
tar czf file.tar.gz files – Create a tar with Gzip compression
tar xzf file.tar.gz – Extract a tar using Gzip
tar cjf file.tar.bz2 – Create a tar with Bzip2 compression
tar xjf file.tar.bz2 – Extract a tar using Bzip2
gzip file – Compresses file and renames it to file.gz
gzip -d file.gz – Decompresses file.gz back to file
Printing
/etc/rc.d/init.d/lpd start – Start the print daemon
/etc/rc.d/init.d/lpd stop – Stop the print daemon
/etc/rc.d/init.d/lpd status – Display status of the print daemon
lpq – Display jobs in print queue
lprm – Remove jobs from queue
lpr – Print a file
lpc – Printer control tool
man subject | lpr – Print the manual page called subject as plain text
man -t subject | lpr – Print the manual page called subject as Postscript output
printtool – Start X printer setup interface
Network
ifconfig – List IP addresses for all devices on the local machine
ping host – Ping host and output results
whois domain – Get whois information for domain
dig domain – Get DNS information for domain
dig -x host – Reverse lookup host
wget file – Download file
wget -c file – Continue a stopped download
SSH
ssh user@host – Connect to host as user
ssh -p port user@host – Connect to host on port port as user
ssh-copy-id user@host – Add your key to host for user to enable a keyed or passwordless login
User Administration
adduser accountname – Create a new user call accountname
passwd accountname – Give accountname a new password
su – Log in as superuser from current login
exit – Stop being superuser and revert to normal user
Process Management
ps – Display your currently active processes
top – Display all running processes
kill pid – Kill process id pid
killall proc – Kill all processes named proc (use with extreme caution)
bg – Lists stopped or background jobs; resume a stopped job in the background
fg – Brings the most recent job to foreground
fg n – Brings job n to the foreground
Installation from source
./configure
make
make install
dpkg -i pkg.deb – install a DEB package (Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint)
rpm -Uvh pkg.rpm – install a RPM package (Red Hat / Fedora)
Stopping & Starting
shutdown -h now – Shutdown the system now and do not reboot
halt – Stop all processes - same as above
shutdown -r 5 – Shutdown the system in 5 minutes and reboot
shutdown -r now – Shutdown the system now and reboot
reboot – Stop all processes and then reboot - same as above
startx – Start the X system
Recommended reading:
Cheat-Sheets.org – All cheat sheets, round-ups, quick reference cards, quick reference guides and quick reference sheets in one page. The only one you need.
LinuxCommand.org – Learning the shell, Writing shell scripts, Script library, SuperMan pages, Who, What, Where, Why
LinuxManPages.com – General commands, System calls, Subroutines, Special files, File formats, Games, Macros and conventions, Maintenence commands, Most Popular Man Pages
Linux Newbie Guide: Shorcuts and Commands - Linux essential shortcuts and sanity commands; Common Linux commands - system info; Basic operations, network apps, file (de)compression; Process control; Basic administration commands, accessing drives/partitions; Network administration tools, music-related commands, graphics-related commands.