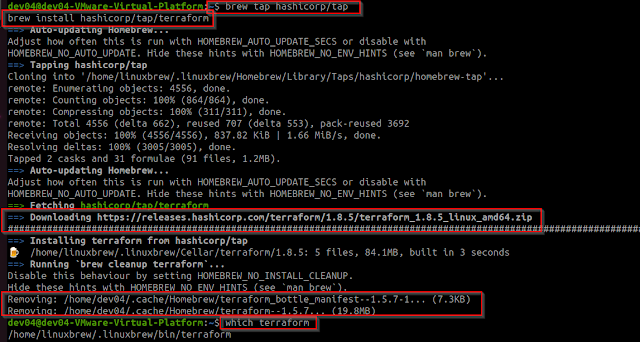
These are the links for us to use to build infrastructure on Azure
- https://github.com/search?q=terraform+build+Azure+cloud
- https://github.com/bridgecrewio/checkov
- Azure Elastic LoadBalancer Terraform - https://github.com/yousafkhamza/terraform-alb
- https://github.com/digihunch/cloudkube
- https://github.com/psmanika/azure-terraform-landing-zone
- https://github.com/scarolan/terraform-foundations-azure
- Precog Azure Project - https://github.com/precog/devops/issues/257
- The issue - https://github.com/orgs/precog/projects/195/views/1
- https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs/resources/virtual_network
- https://registry.terraform.io/modules/Azure/vnet/azurerm/latest
- https://registry.terraform.io/modules/Azure/network/azurerm/1.0.0
- https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs/resources/virtual_network_gateway_connection
- https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/azurerm/latest/docs/resources/virtual_network#example-usage
- https://github.com/search?q=azurerm+vnet
- https://github.com/kumarvna/terraform-azurerm-vnet
- https://github.com/Azure/terraform-azurerm-vnet
- Azure documentation - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/terraform/get-started-cloud-shell-bash?tabs=bash